What is teeth whitening?
Teeth whitening aims to lighten the colour of the teeth. This treatment is performed in an attempt to whiten or lighten the shade of teeth that appear dark or discoloured. There are many reasons why teeth may be discoloured. Dental professionals are best placed to diagnose the reason for tooth discolouration and provide advice on whether tooth whitening will be an effective treatment.
What causes tooth staining?
Over time, your teeth can go from white to not-so-bright for a number of reasons. Common reasons include foods and drinks, tobacco, age, medications and trauma. Food and drinks such as coffee, tea and red wine are some major causes of staining. The intense colour pigments of these drinks are called chromogens. The chromogens attach to the white tooth enamel causing it to appear darker.
The chemicals tar and nicotine in tobacco are well known causes of tooth discolouration, turning the teeth a yellowish colour. As people age, the enamel layer can become thinner allowing the inside dentine to show through. Dentine is yellowish in colour and therefore makes the tooth appear darker when the enamel thins.
Injury to the teeth can cause the affected tooth or teeth to become darker over time. The injury can cause the tooth to create more dentine to protect the dental pulp but this can make the tooth visually appear darker. Trauma can also cause blood from inside the tooth to leak into the surrounding tooth structure leading it to appear discoloured.
Some medications are known to cause tooth staining as a side effect. Young children who are exposed to antibiotics like tetracycline and doxycycline when their teeth are forming (either in the womb or as a baby) may have discoloration of their adult teeth later in life.
Extrinsic staining
Stains that are on the outside surface of the tooth are known as extrinsic stains. Examples of causes of these stains can include tea, coffee, red wine and smoking. Depending on the type of staining, it may be able to be removed while brushing with whitening toothpaste as well as professional dental cleaning or by chemical treatment.
Intrinsic staining
Staining that is located inside the tooth’s structure is known as intrinsic staining. Potential causes can include medications taken during tooth development, trauma causing blood from inside the tooth to leak into the surrounding tooth structure, amalgam (metal) fillings or root canal treatments.
Removing stains that are based inside the tooth can be very difficult if trying to treat from the outside surface. Depending on the cause of the tooth discolouration, treating the tooth from the inside may be possible.
Teeth that have been injured and undergone root canal treatment may appear discoloured. This is an example of when tooth whitening treatment can be used on the inside of the tooth. The whitening treatment is placed in the centre of the tooth where the dental nerve was once located. It is left inside the tooth for several days before being cleaned out and the tooth fixed with a filling. This treatment is called internal bleaching and can only be done by a dental professional. The internal bleaching treatment may be followed by a crown or veneer treatment.
Whitening ingredients
Teeth whitening completed by dental professionals involves chemically treating the teeth with hydrogen peroxide or carbamide peroxide. These are the main ingredients used in tooth whitening products by dentists in Australia. The strength of the tooth whitening gel used depends on whether the treatment is completed at a dental clinic or at home. Higher strength whitening gels can be used by dentists.
Hydrogen peroxide is also included in some ‘whitening toothpastes’ at levels of 1 to 5%.
Phthalimidoperoxycaproic acid, more easily referred to as PAP, is another ingredient that can be found in toothpastes aimed at whitening teeth. This is organic peroxide that acts like a bleaching agent.
Treatment options
There are two main ways a dental professional can provide treatment to whiten teeth – ‘in-chair’ or ‘take-home’ whitening.
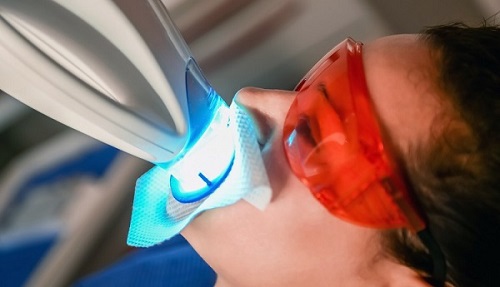
In-chair teeth whitening
In-chair or in-office teeth whitening treatment is performed by a dentist whilst you are sitting in the dental chair. This treatment uses strong hydrogen peroxide gel and often a light placed over the teeth. You should leave your dental appointment with whiter teeth. Your dentist may also suggest continuing using take-home whitening treatment to maintain the whiter tooth colour at home.
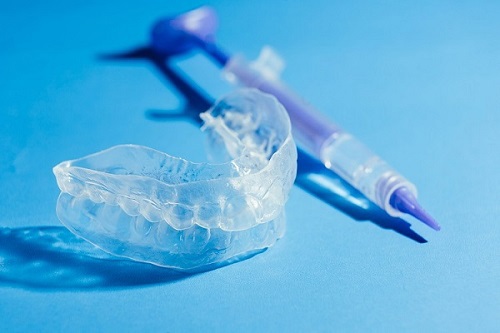
Take-home teeth whitening
Take-home teeth whitening treatment is completed at home by the patient under the supervision of their dentist. The dentist will custom-make thin, plastic trays that fit over the surface of your teeth only. At home, the teeth whitening gel is placed in these trays and then worn for a set amount of time. Your dentist will advise you on how to place the whitening gel in the trays, how much to use each time and how long to wear the trays for each time also. This method of teeth whitening does take longer than treatment completed in the dental clinic, but this does not mean that the final result is better or worse. Your dentist will discuss your options and provide advice on what type of treatment is best for you.
Tooth whitening toothpaste
Whitening toothpastes work by helping to reduce stains present on the outside surface of the tooth enamel. The toothpastes often contain special abrasives and/or whitening agents. Some toothpastes include the ingredient sodium hexametaphosphate, which can work to repel stains from the surface of teeth. Hydrogen peroxide a common ingredient in teeth whitening gels are also added to toothpastes that aim to lighten the colour of teeth, at levels from 1 to 5%. Phthalimidoperoxycaproic acid, more easily referred to as PAP, is another ingredient that can be found in toothpastes aimed at whitening teeth. It is organic peroxide that acts like a bleaching agent.



